Securing Tomorrow’s Connectivity: The Advantages of Enhancing Your Cabling Infrastructure

The digital transformation is sweeping across industries. It has made connectivity more important than before. The pandemic has only made it clearer that people need to stay connected virtually. That way, they can check on their loved ones or colleagues during hard times. Data and bandwidth demands continue to rise. No one wants to keep subscribing to providers that offer poor connectivity.
Enterprise networks and data centers must upgrade their cabling infrastructure to keep pace. Otherwise, they are in danger of becoming obsolete. Even startup providers may outperform them if they fail to adapt.
This article explores the key innovations in cabling technology that will power tomorrow’s hyperconnected world. There is much to discuss, such as:
- The history and evolution of cabling
- Advancements in Fiber Optics
- The significance of Cat6 and Cat6a Cabling
- PoE and IoT
- Eco-friendly cabling solutions
The Evolution of Cabling: From Copper to Fiber Optics
Copper cables have been the backbone of connectivity since the early telephone networks. But global IP traffic is expected to reach 4.2 zettabytes per year by 2022. Copper cables are reaching their limits. This has fueled massive investments in fiber optic technology. It uses light to send data at ultra-high speeds over long distances.The fiber optics market is projected to grow from $6.7 billion in 2020 to $9.8 billion by 2025. More organizations will “future-proof” their infrastructure.
Advancements in Fiber Optic Technology
Fiber optic technology has evolved tremendously over the past decade. It is thanks to continued enhancements in materials and manufacturing. If an individual lives in Florida, network cabling Miami specializes in providing robust network cabling infrastructure across surrounding regions. Subscribers can avail of high-bandwidth multi-mode and single-mode optical fibers. Each now boasts capacities ranging from 40Gbps to 1Tbps.
Certain innovations also enable many signals to be sent over a single fiber:
- Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)
- Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM)
DWDM enables up to 80 channels of data to be multiplexed into one fiber cable. It does so by exploiting different wavelengths of laser light.
New transceivers are also enhancing efficiency. There are small form factor pluggable (SFP) transceivers. They allow different interfaces to be adapted to fiber ports:
- Ethernet
- Fibre Channel
- SONET
Optical fiber connectors have become smaller and higher-performing as well.
Such advancements enable fiber networks to handle massive workloads. And it happens at ultra-low latency with minimal data loss. Fiber optics boast at least these three features:
- They are up to 100 times faster than copper cables.
- They can transmit data over longer distances.
- They are far less prone to electromagnetic interference.
This makes them indispensable for lightning-fast and reliable data center and enterprise connectivity.
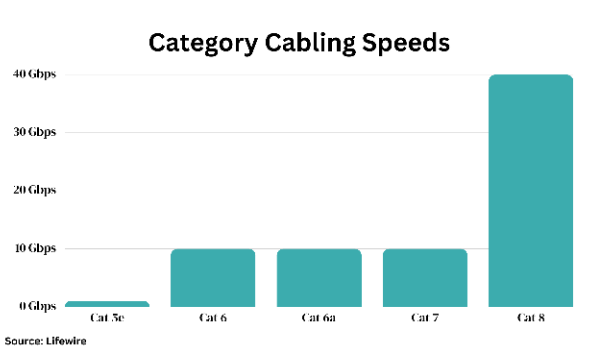
The Significance of Cat6 and Cat6a Cabling
Fiber optic backbones shuttle data across states and continents. Meanwhile, copper cables send data to buildings and campuses. Category 6 and Category 6a cables are becoming the de facto standards. Although limited to 100 meters, Cat6 supports bandwidth frequencies up to 250Mhz. Meanwhile, Cat6a can reach 500Mhz frequencies at the same distance.
This makes them ideal for handling high-speed applications such as:
- 4K video
- Emerging IoT ecosystems
- Next-gen wireless technologies
They boast of the following:
- Performance
- Cost-efficiency
- Ease of installation
They ensure that Cat6 and Cat6a will play a key role in future enterprise and data center upgrades.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) and the IoT Revolution
Another cabling breakthrough powering tomorrow’s hyperconnected infrastructure is Power over Ethernet (PoE). This allows network cables to deliver both data and power simultaneously. IoT devices proliferate across these places:
- Homes
- Offices
- Cities
PoE eliminates the need for separate power sources. PoE is now widely integrated with the following:
- Security cameras
- WiFi access points
- IoT sensors
- Lighting systems
The global IoT market is projected to reach $1.1 trillion by 2026. Thus, The demand for PoE-capable structured cabling is expected to skyrocket. It has an ability to “plug-and-play” thousands of devices. That gives it an edge over traditional power delivery.
Structured Cabling Systems
To enhance next-gen connectivity, enterprise networks must adopt a structured cabling system (SCS). This integrates all low-voltage applications onto one comprehensive infrastructure:
- Voice
- Data
- Video
- Security
- Building automation
Bulk horizontal and backbone cables are neaty consolidated. They use patch panels and cabling racks. SCS maximizes these factors across network infrastructures:
- Efficiency
- Scalability
- Device convergence
It also simplifies troubleshooting, maintenance, and future upgrades. Leading network organizations recommend incorporating SCS designs wherever possible.
The Convergence of Wired and Wireless Networks
Wireless technologies grab headlines. Even the most robust WiFi networks rely heavily on the underlying cabling infrastructure. Fiber and copper cabling are essential for linking wireless access points and routers. They also provide vital backhaul connectivity from base stations to data centers.
Cables enable the error-free data transmission necessary for ultra high-frequency wireless networks. At the same time, they are isolated from electromagnetic interference. Thus, they are far from fading into obsolescence. Advanced cabling is guaranteeing both the wired and wireless networks of the future.
Cabling Infrastructure for Smart Buildings
Specialized cabling solutions also hold great promise for smart buildings. The Internet of Things also look forward to what specialized cabling has to offer. Plenum-rated cables enable safe installation in building HVAC systems. They can securely connect sensors and automation devices. Structured cabling provides an organized pathway for thousands of IoT endpoints. Power over Ethernet enables device convergence, while eliminating cumbersome power supplies.
Companies now offer industrial Ethernet switches and routers purpose-built for harsh smart building environments. Smart green buildings are becoming mainstream; therefore, advanced cabling systems will provide the robust connectivity they need.
Cable Testing and Certification
Deploying next-gen cabling infrastructure requires rigorous testing. Cabling installers use high-performance testers to certify that cables meet industry standards like Cat6/6a. They also test parameters like the following:
- Insertion loss
- Near-end crosstalk (NEXT)
- Return loss to detect any flaws
Such testing ensures networks perform optimally despite growing transmission speeds and frequencies. It also reduces interference between cables in high-density data centers.Regular retesting helps identify errors before they cause service outages. In a hyperconnected world, failure to properly test cabling invites disaster.
Eco-Friendly Cabling Solutions
Another positive trend is the push toward sustainable networking infrastructure. Top cable manufacturers now focus on:
- Energy efficiency
- Recyclable materials
- Environmental Product Declarations
Data centers also conserve electricity by routing cooling strategically using hot aisle containment. ICT is estimated to account for 2% of global CO2 emissions by 2040. Deploying eco-friendly cabling and data centers is becoming imperative. It proves networks can deliver world-class connectivity without sacrificing ecological well-being.
Securing Connectivity Using Modern Cabling
Organizations transfer sensitive data and systems onto networks. This means cabling infrastructure must evolve to combat cyberthreats. Modern fiber and copper cabling offer embedded data encryption to protect against tapping. Cloud-based network access control and intrusion detection integration provide additional safeguards. And secure cabling policies reduce disruption:
- Mandatory test certification
- Redundancy
- Physical access controls
Breaches are growing costlier. Building and upgrading to secure resilient cabling is no longer optional.
Conclusion: Invest Now to Secure Tomorrow
From smart cities to telehealth, our digital future will depend on high-speed connectivity. Modernizing cabling infrastructure with these solutions will prepare organizations for this hyperconnected reality:
- High-capacity fiber optics
- Cat6/6a Ethernet
- Power over Ethernet
- Structured cabling systems
Companies that delay upgrades risk facing outages, bottlenecks, and vulnerabilities in the future. Now is the time to invest in next-generation cabling.
FAQs
- How does advanced fiber optic technology impact the efficiency of data centers?
The massive leaps in these factors translate to enhanced efficiency:
- Fiber optic bandwidth
- Capacity
- Speed
High-speed fiber backbone connections prevent bottlenecks. Meanwhile, low-latency fiber to the rack improves data transmission between servers. Fiber optic networks also provide vast scalability using consolidation products like:
- DWDM
- WDM
This allows capacity expansion without costly re-cabling.
- What key factors drive the adoption of PoE in IoT and smart building applications?
There are three key factors:
- PoE simplifies the installation and reduces cabling costs of IoT devices. This is due to how it delivers power and data over a single Ethernet cable. This plug-and-play capability accelerates deployment.
- PoE enables device mobility. Powered devices can be moved without installing new power supplies in each location.
- Backup power from centralized UPS systems can be delivered to devices over Ethernet. This makes the IoT ecosystem more robust and resilient to power outages.
Together, these factors are accelerating PoE adoption across the following:
- Smart homes
- Offices
- Other connected environments
- In terms of cybersecurity, how does cabling infrastructure ensure data protection during transmission?
Modern cabling infrastructure is integrating advanced cybersecurity capabilities, including:
- Encryption protocols
They provide encryption at the physical cabling layer to secure data transfers.
- Network Access Control solutions
They can integrate with cabling. It will restrict unauthorized device access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems
They can also leverage cabling to identify malicious network activity.
- Robust physical access control policies
These are used for cabling infrastructure to prevent tampering.
Organizations can enhance data protection and compliance while sending sensitive information across networks.



