10 Best Practices for Elderly Medication Management
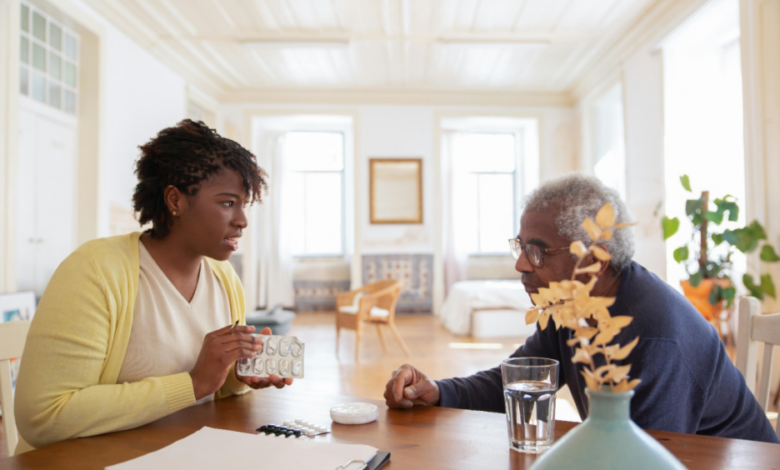


Managing medications is a crucial aspect of healthcare, especially for the elderly who often deal with multiple prescriptions. As age advances, so does the complexity of medical regimens, making it challenging for seniors to keep track of their medications effectively. This can lead to dangerous mistakes, such as overdoses or missed doses, both of which can have serious consequences on their health. The goal of this article is to explore practical steps that can improve medication management among elderly populations, ensuring their safety and enhancing their quality of life.
1. Understanding Medications
One of the first steps in effective medication management is ensuring that seniors fully understand what medications they are taking and why. It’s important for both the elderly and their caregivers to have a clear grasp of each prescription’s purpose. This understanding can significantly reduce the risk of medication errors and increase adherence to prescribed treatment plans. Caregivers can assist by organizing consultations with healthcare providers where they can ask questions and obtain straightforward explanations about the medications.
2. Regular Consultations with Healthcare Providers
Regular interactions with healthcare professionals are vital for the elderly to manage their medications properly. These consultations provide an opportunity to review current prescriptions, discuss any side effects, and make necessary adjustments to the regimen. Frequent check-ups ensure that medications are still appropriate as health conditions evolve over time. Encouraging seniors to speak openly with their doctors and pharmacists about their medications can lead to better health outcomes and reduced hospital visits.
3. Implementing Medication Synchronization Programs
A highly effective strategy for simplifying medication regimens is through synced Rx, which is essentially when medication is synchronized so that all of a patient’s prescriptions can be picked up from the pharmacy on the same day each month. This is commonly referred to as MedSync. These programs reduce the likelihood of forgetting to refill prescriptions and improve adherence. Programs such as MedSync not only streamline the process of managing multiple medications but also provide an added layer of support from pharmacy staff who monitor adherence and can offer timely consultations.
4. Using a Pill Organizer
Pill organizers can greatly assist in the daily management of medications. They help the elderly keep track of whether or not they’ve taken their scheduled doses. These organizers come in various forms, from basic daily compartments to more advanced models that can be set up for weekly use. Choosing the right pill organizer depends on the complexity of the medication regimen, and caregivers can help in selecting the most suitable type that matches the individual needs of the elderly person.
5. Setting Up Reminders
Setting up reminders can further enhance medication adherence. Whether it’s through the use of technology like alarms on smartphones or digital watches, or more traditional methods like calendars and note cards, reminders serve as an effective prompt for seniors to take their medication at the correct times. Caregivers can help set these reminders in accordance with the medication schedule prescribed by healthcare professionals.
6. Maintaining an Updated Medication List
Keeping an updated list of all medications is crucial. This list should include details about the dosages, the timing of doses, and any special instructions. It’s important for both the senior and their caregivers to maintain this list and ensure it’s readily available during doctor visits or in an emergency. An accurate medication list helps healthcare providers make informed decisions and can prevent potentially dangerous drug interactions.
7. Educating on Side Effects
Educating the elderly about potential side effects of their medications is crucial. Understanding what side effects can occur, and recognizing them early, can help prevent further complications. Seniors and their caregivers should have discussions with healthcare providers about what symptoms to watch for. If any adverse effects are noticed, it is imperative to contact a healthcare provider immediately. This proactive approach can help manage side effects more effectively, ensuring that they do not escalate into more serious health issues.
8. Proper Storage of Medications
Storing medications properly is key to maintaining their effectiveness. Many medications need to be stored at specific temperatures and away from light and humidity. Seniors should be instructed on the correct storage methods for each of their medications. For instance, some might need refrigeration, while others should be kept in airtight containers. Proper storage also helps in preventing accidental misuse or ingestion by others, particularly if there are children in the house.
9. Reviewing Medications Periodically
The medical needs of seniors can change over time, which may necessitate adjustments in their medication regimens. Regularly reviewing these regimens with a healthcare provider ensures that all medications are still necessary and working effectively. It also provides an opportunity to de-prescribe unnecessary medications, reducing the risk of adverse drug interactions and side effects. Periodic reviews help keep the medication list current and relevant to the senior’s current health condition.
10. Avoiding Self-Medication
It’s important for elderly individuals to avoid self-medicating, especially with over-the-counter drugs, without first consulting a healthcare provider. Many common non-prescription medications can interact negatively with prescription drugs, leading to potentially harmful effects. Seniors should be encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about all substances they’re considering taking, including herbal supplements and over-the-counter medications.
Securing Safe Practices
Effective medication management is a crucial aspect of healthy aging. By implementing best practices such as educating seniors about side effects, ensuring proper medication storage, and periodically reviewing medication regimens, elderly individuals can significantly improve their medication adherence and overall health. Additionally, avoiding self-medication and accessing professional consultations are vital steps in maintaining safety.
It is essential for family members and caregivers to be actively involved in the medication management process. They can offer invaluable support by facilitating discussions with healthcare providers, helping manage medication schedules, and ensuring that the seniors’ living environments are conducive to safe medication practices. By fostering an environment of open communication and diligent care, we can help ensure that the elderly manage their medications safely and effectively, thereby enhancing their quality of life and independence.